Electronic business is also known as “e-business” or “e-commerce.” It is when information and communication technologies are used to support various business activities.
Electronic business is viewed as only a subset of the overall electronic business strategy, where the strategic focus is placed more on implementing business functions using electronic capabilities.
Its process encompasses the entire value-added chain, from cooperation with trading partners to electronic order processing, electronic purchasing, customer service processing, and supply chain management. With the support of special technical standards, companies can exchange data. With the various electronic business software solutions, it is possible to integrate business processes between and within companies. Internet, extranets, web, intranets and their combination facilitate it.
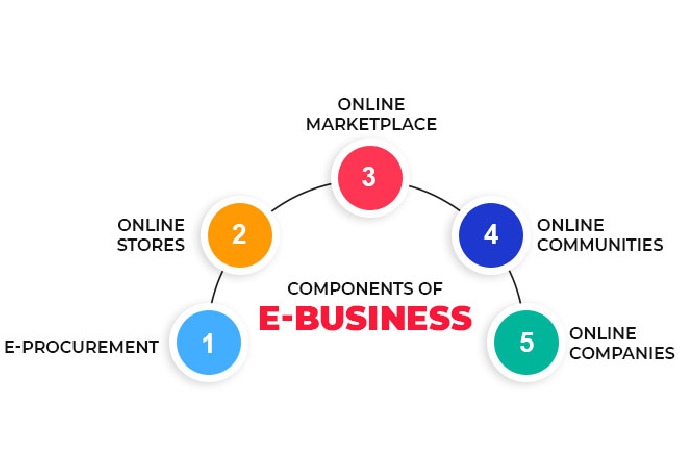
Electronic business includes e-commerce, e-marketing, and e-commerce:
1) Ecommerce:
All aspects of business processes are simplified through the use of Internet technology.
2) E-marketing:
The company’s online presence can be built and displayed by providing detailed information. Most small businesses these days engage in e-marketing.
3) Ecommerce:
It automatically supports customer inquiries, makes payments, sells services and products online, and handles transaction details.
4) Electronic Operations:
Business efficiency within the functional departments of an organization is optimized through several steps. The supply chain between the leading suppliers and the company is also streamlined.
E-Business = E-Marketing + Electronic business+ E-Operations
Electronic processes
E-Business processes can be roughly divided into three categories:
1) Production:
This category includes processes such as trade purchases, supplier ordering and inventory replacement, payment processing, supplier transactions, and processes related to production control, etc.
2) Relationship with the customer:
This category of business processes includes product marketing and promotion, online product sales, customer order processing, customer payments, customer service, customer service, etc.
3) Internal administration:
Business processes in this category typically consist of managing employees, recruiting employees, training, and communicating information within the organization between departments such as production and sales to improve departmental productivity.
Electronic business and electronic business are often being replaced.
Characteristics of electronic business
The characteristics of the electronic business are explained below:
1. Omnipresence:
Electronic business is widespread, which means it is available anytime, anywhere. It prevents the free market from being confined to a physical space and allows shopping from a computer (e.g. desktop, laptop). The result is called the market. Place.
For consumers, ubiquity lowers the transaction costs of exploring products in a marketplace. Consumer. They can access any information wherever they want, regardless of location. The buyer no longer needs to spend time and money travelling to a market, and it saves the cognitive energy required to transact in a market space.
2. Global Reach:
Electronic business technologies allow a business to cross geographic borders worldwide in a much more convenient and effective way than traditional commerce. Companies worldwide are realizing higher profits and business results by expanding their business with electronic solutions. As a result, the potential market for it retailers is roughly the size of the online population.
3. Universal standards:
Universal standards are standards shared by all nations of the world. These are technical standards for the Internet to conduct electronic business. It allows everyone to connect on the same “level” and provides network externalities that benefit everyone. Consistent technical standards reduce entry costs and minimize search costs.
4. Interactivity:
E-commerce technologies enable two-way communication between customers and suppliers, making them interactive. It is a significant feature of e-commerce technology over the traditional business technologies of the 20th century.
5. Information Density:
Information density refers to the total amount and quality of information available to all buyers and sellers in the marketplace on the Internet. The Internet increases information density enormously, providing consumers and retailers with better quality information. Electronic commerce technologies increase the accuracy and timeliness of the data.
For example, the flipkart.com store has a variety of products with prices.
6. Assets:
Richness refers to the complexity and content of a message, and wealth means all business activities and experiences carried out through various messages.
For example, text, images, videos, sound, links, SMS (Short Message Services) etc.
7. Customization:
Ecommerce Technology Offerings, Personalization. Personalization means tailoring marketing messages to specific individuals by personalizing them based on the customer’s personal information such as name, interests and past purchase history. Products or services may be modified based on user choice or past purchase history.